Applications
Reason to Choose
Some people who use paper labels for information visualization are concerned about the environmental impact of paper label disposal. In such cases, electronic paper tags may be the best alternative. Since electronic paper tags can be used repeatedly without batteries, they are an environmentally friendly solution that does not generate waste due to paper and battery disposal. In addition, since the electronic paper is rewritten using UHF RFID, the displayed information can be updated without contact. If you need to visualize information but are concerned about the environment, please consider adopting electronic paper tags.
1.Battery-less, eliminating the need for battery replacement
Electronic paper does not require power to display images after rewriting, but power is needed to rewrite the display on electronic paper. battery-less electronic paper tags are realized by wirelessly supplying power via UHF band RFID.
- Requires periodic battery replacement
- Cumbersome and involuntary work, such as managing the timing of battery replacement, is required
- Man-hours required to replace batteries


- Wireless power supply eliminates the need for batteries
- No need for work related to battery replacement
- Zero man-hours required for maintenance
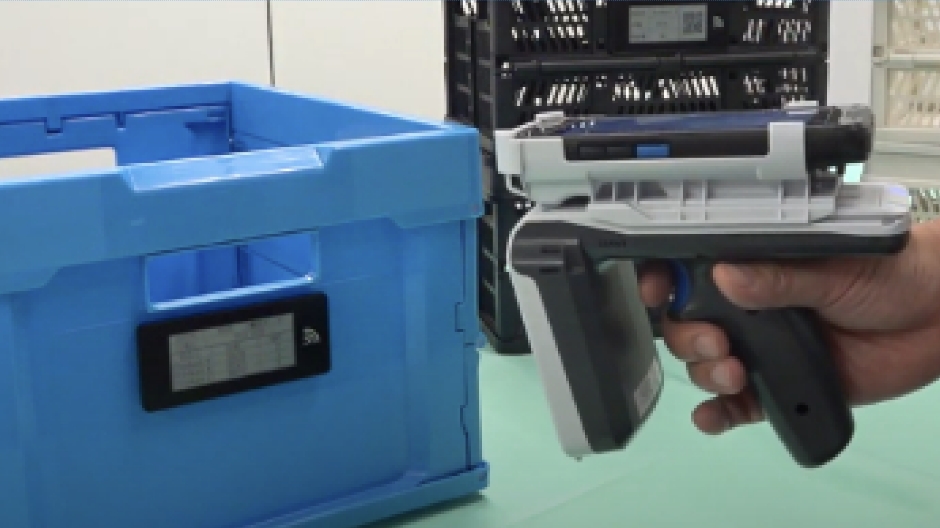
2.Using the UHF band, ePaper can be rewritten without contact.
By using UHF RFID, contactless rewriting of electronic paper can be realized. This makes it possible to rewrite the paper while it is attached to an object or a moving object.
- Paper labels
ー Paper labels require printing and re-covering - HF band electronic paper tag
ー Rewriting requires contact with the transmitter (R/W)


- Repeatable, so there is no need for replacement and no disposal cost
- Contactless rewriting is possible because of the use of the UHF band.
- Rewritable even when attached to a mobile device
ePaper Tag Rewriting Video
3.RFID tag with large capacity (8kB) user memory
The large memory capacity makes it possible to store work history and other information on RFID tags; by using RFID tags as data carrier devices, information can be exchanged without the need for networking.
- General tags have low user memory capacity
- Data sharing between companies requires data exchange over a network
- Network construction is required to store work information/history for production control
- Other companies' high-capacity memory tags use EEPROMs, which take a long time to write



- No need to build a network because information can be stored in a large-capacity memory.
- Can be used as a data carrier device
- Uses FeRAM, which can be written at high speed, so writing time with RFID is short.
- Data that is not to be displayed or not required to be displayed can be stored in memory.

4.3 roles in one device: written information, 1D/2D barcodes and RFID
Paper labels are often used when textual information needs to be displayed for information visualization. Electronic paper tags not only display information in the same easy-to-read manner as paper labels, but can also function as RFID.
- Paper labels are used to display text information and one- and two-dimensional barcodes.
- If the paper becomes dirty and cannot be read, it must be replaced.
- A separate device must be added to provide RFID functionality.


- ePaper Tags can be wiped clean even if dirt adheres to the surface.
- Textual information and one- and two-dimensional barcodes can be displayed, just as on paper labels.
- RFID functionality allows for detection of objects, confirmation of passage, and storage of information.


